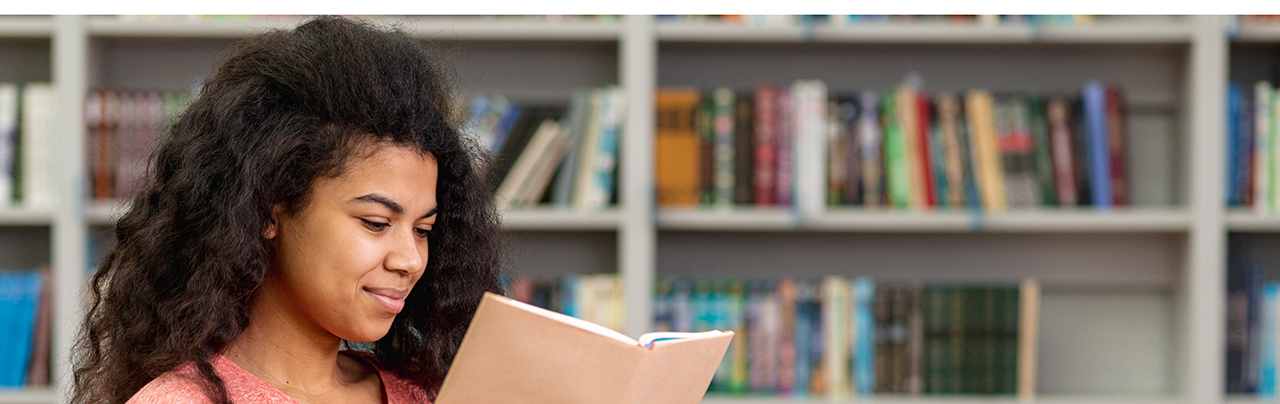
Enterprise Risk management (ERM) is a broad field with a wide array of concepts, methodologies, and jargon. One can learn more about all these concepts along with their practical application with IRM’s Global Enterprise Risk Management Qualifications (Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3) however here are ten risk terms that are not commonly known outside of the discipline:
Value at Risk (VaR): VaR is a statistical technique used to measure the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over a specific time frame. It estimates the potential loss that could happen in an investment portfolio due to adverse market movements.
Risk Factor: A Risk Factor is a situation or condition that increases the likelihood or impact of a risk event occurring. It can pertain to internal or external elements.
Tail Risk: This term refers to the risk of an extreme event that will impact the tail end of a probability distribution. These risks are not very frequent, but they can have a severe impact when they occur.
Expected Shortfall (ES): ES is a risk measure that quantifies the expected value of the tail loss given that the event has exceeded the VaR threshold. It’s a way of estimating the potential losses in very bad scenarios.
Concentration Risk: This is the risk associated with any single exposure or group of exposures with the potential to produce large enough losses to threaten a financial institution’s health or ability to maintain its core operations.
Bow-Tie Analysis: This term refers to a risk evaluation method that visualizes causal relationships in complex systems. A bow-tie diagram does two things primarily: it gives a visual summary of all plausible accident scenarios that could exist around a certain hazard, and it shows what an organization does to control those scenarios.
Operational Risk: It refers to the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems, or from external events. This can include various types of risk such as fraud risk, legal risks, physical or environmental risk.
Risk Register: Also known as a Risk Log, it is a document that lists all identified risks, including descriptions, category, probability of occurring, potential impact, mitigation actions, etc. It is a crucial component of the overall risk management framework.
3rd Party Risk Management (TPRM): This term deals with the strategies for dealing with risks associated with relying on third parties, from contractors and consultants to suppliers and partners.
Risk Heat Map: A Risk Heat Map is a data visualization tool for presenting the outcome of a risk evaluation process. Risks are plotted on a grid where the x-axis represents the likelihood of the risk and the y-axis represents the impact of the risk.
These terms are by no means exhaustive but can provide a deeper understanding of risk management’s complexity. By being aware of these, individuals can better anticipate and prepare for various scenarios that could affect their operations. Start with IRM’s Global Level 1 ERM Foundation Examination.