Risk management is an important aspect of pharmaceutical microbiology, as it helps to ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. Microbial contamination can have serious consequences, including illness or death in patients who consume contaminated products. Therefore, it is crucial that pharmaceutical manufacturers implement effective risk management strategies to prevent and mitigate the potential for contamination.
There are several steps involved in risk management in pharmaceutical microbiology. The first step is to identify the potential sources of contamination. This includes identifying the raw materials, equipment, and environment that could potentially harbor microorganisms that could contaminate the final product. This information can be obtained through a variety of methods, including microbiological testing, environmental monitoring, and risk assessments.
Once the potential sources of contamination have been identified, the next step is to implement controls to prevent or mitigate the risk of contamination. This can include implementing good manufacturing practices (GMPs), such as proper sterilization and disinfection procedures, as well as maintaining a clean and controlled environment. It is also important to properly train employees on GMPs and to regularly audit and monitor the effectiveness of these controls.
One key aspect of risk management in pharmaceutical microbiology is quality control testing. This involves testing raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products to ensure that they are free of contamination. There are several types of quality control tests that can be used, including microbiological assays, bioburden testing, and endotoxin testing. These tests help to ensure that products meet the necessary quality and safety standards.
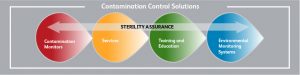
Another important aspect of risk management is the implementation of a recall plan. In the event that a product is found to be contaminated, it is essential that it be quickly and efficiently recalled to prevent further harm to patients. The recall plan should outline the steps that need to be taken to identify and remove the contaminated product from the market, as well as any necessary notifications to regulatory agencies and the public.
In addition to these strategies, it is also important to have a contingency plan in place to address unexpected events or emergencies. This may include identifying alternative sources of raw materials or equipment or establishing procedures for quickly identifying and addressing any potential contamination issues.
One of the biggest challenges in risk management in pharmaceutical microbiology is staying up-to-date with current regulations and guidelines. These can vary from country to country and may change over time, so it is important for pharmaceutical manufacturers to keep abreast of these changes and ensure that their risk management practices are in compliance.
Effective risk management in pharmaceutical microbiology is essential to ensure the safety and quality of pharmaceutical products. By identifying potential sources of contamination, implementing controls to prevent or mitigate the risk of contamination, conducting quality control testing, and having a recall plan and contingency plan in place, pharmaceutical manufacturers can help to protect the health and well-being of patients.
In addition to the strategies mentioned above, there are a few other risk management practices that are important to consider in the field of pharmaceutical microbiology.
One is the use of aseptic processing techniques, which are used to prevent the introduction of microorganisms into sterile products. Aseptic processing involves creating a sterile environment in which to manufacture the product, using sterilized materials and equipment, and following strict protocols to minimize the risk of contamination. This is especially important for products that are intended for injection or other routes of administration where even a small amount of contamination could be harmful to patients.
Another risk management practice is the use of quality assurance programs. These programs involve the development and implementation of policies and procedures that ensure the consistent production of high-quality products. This can include conducting regular audits and inspections, implementing a system for tracking and investigating quality issues, and establishing a process for identifying and correcting problems.
Finally, it is important to consider the use of risk assessment tools in pharmaceutical microbiology. These tools, such as hazard analysis and critical control point (HACCP) systems, help to identify and assess potential risks and determine the appropriate controls to prevent or mitigate those risks. By regularly conducting risk assessments, pharmaceutical manufacturers can identify and address potential vulnerabilities in their processes and ensure the safety and quality of their products.
In conclusion, risk management is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical microbiology. By implementing controls to prevent and mitigate the risk of contamination, conducting quality control testing, and having a recall plan and contingency plan in place, pharmaceutical manufacturers can help to protect the health and well-being of patients. Additionally, the use of aseptic processing techniques, quality assurance programs, and risk assessment tools can further enhance the effectiveness of risk management practices in this field.