“Starting to run fast, only to reach an end”
5G or Fifth Generation, is the latest and fastest wireless mobile device technology being initiated in 2019. Today, 5G is expected to enhance the performance, durability, and efficiency of mobile devices with a wide range of new applications and software with build-up of e-services as well.
5G or the fifth-generation technology communication for broadband cellular networks is the fastest network and communication technology for 21st-century people succeeding the 4G network.
5G possesses greater speed but could easily take us to our end. Although it represents an unfathomable standard in the telecommunication and digital sector, the hesitancy of data privacy is a huge concern as the data exodus could be accessed with one hand and in seconds. Every revolution always brings stress and hurdles with itself. Till 4G, the network had minimal changes but the new changes with technological advancement is a mirage of easiness to people as it has many more repercussions than the previous conglomerates.
The USA is currently leading the way on 5G as it imposes great risks to an individual as well as to the government of a country and thus the security threat to the pan world out there.
Implementation of 5G network will introduce risks in mainly two areas: Health and Cyber
Probability of exposure or loss resulting from a cyber-attack or data breach on your organization.
- Data Sharing: The significant key area of risk under 5G is the data compromise that has the huge possibility to steal data of innocent people by third parties with easy access to their device. It is due to the increased spread of intermediaries in this network as well as the software involved to get access to the data network. This poses a large threat to the privacy of the individuals as well as of the nation’s own government.
- The Connectivity Compromise: The connectivity compromise also referred to as availability compromise is a platform where an attack shifts a network offline. Governments always fear threats of availability compromise, as if they are targeted at energy or defense infrastructure, it could lead to significant implications on national security.
- Speed is a two-edged sword: Speed could be an irony. It can cut for us as well as against us. 5G is as fast as a bullet but this also means that stealing the data from a device will take the hacker far less time. After thorough scrutinization, data compromise can occur through a truly high-speed without monitoring being initiated due to high traffic at hands of cyber terrorists.
- Internet Of Things(IoT): Increasing the number of online and integrated objects in a single network would naturally increase the potential threats and vulnerabilities, as unauthorized users would now have far more points of accessible entry into the network. In addition, the types of devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops are inter-connected with one another and thus, can be integrated into the same system. This would further complex the task of ensuring cybersecurity on each device.
- Lack of end-to-end encryption: A lack of end-to-end encryption in the presence of multi communication channels connecting 5G/4G and Wi-Fi will get attackers a step forward to intercept data. As such, 5G must integrate end-to-end encryption. This would create a communication timeline where only devices that exchange information together can access the messages.
- Short Range Towers: The 5G network would require the infrastructure of a high number of short-range physical cell towers. These towers will then become a new deployment of physical targets that hackers can exploit. They will have dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS), which allows specific layers of the network to be accessed for data transmission. This would mean that each can be attacked independently and will require a dynamic cybersecurity solution.
- Unaddressed past inefficacies: The main issues already affecting previous generations of mobile technology, such as LTE, have not been addressed in 5G standards. One, in particular, is the ability to intercept pre-authenticated messages between the user’s base station and the cell tower which is still part of the 5G specifications, and proposed technicians would allow attackers to intercept unencrypted messages.
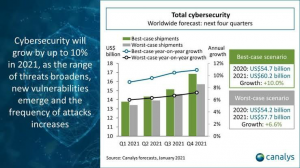
The graph below shows the cybersecurity growth in past years and the possible 2021 data breach that could increase up to 10% and more if 5G technology is initiated.
Source: Canalys Forecasts, 2021 January
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities could give a free hand to attacks and thus could invite a disaster.
Botnet Attacks allow inter-connected devices to get controlled in order to launch a massive cyber-attack. There’s another, known as Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attack that disingenuously intercepts and alters communications between two parties.
Health and Environmental Risks
5G could act as a multi-way threat by not only impacting privacy but also the health and lifestyle of an individual. Millions of studies link low-level wireless radio frequency of 5G radiation exposures to a long list of adverse biological effects.
The World Health Organisation(WHO) in 2011, classified low radiofrequency radiation as a 2B carcinogen and thus a threat to the world.
Recently, the National Toxicology Program, the whopping $25 million program also concluded that radiofrequency radiation(currently used by cell phones) can cause cancer.
As 5G falls into the category of utilizing the middle of above and below frequency bands and its capacity utilization of high frequencies has its own implications.
Here is the review of 5G radiation could impact Health and the Environment:
Electrosmog also called electro-magnetic fields (EMF) or microwave radiation or electromagnetic radiation(EMR) refers to human-made radiation which is a pollutant.
People cannot see it or smell it and therefore, it poses a great threat. The high frequencies with short-range intensities create a more intensified denser soup of electrosmog, as shown below:
| Layer | Frequencies | |
| Coverage | MHz: 600,700,800,900
GHz: 1.5, 2.1, 2.3, 2.6 |
|
| Capacity | Europe: 3400-3800(MHz)
China: 3300-3600(MHz) USA: 3100-3550(MHz) Japan: 3600-4200(MHz) |
|
| High Throughput |
Europe: 24.25-27.5GHz China: 24.25-27.5GHz USA : 27.5-28.35GHz Japan: 27.5-28.28 GHz |
Source: Latest on 5G spectrum EMFields
With the accessibility of connectivity between trillions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, it is crucial that government and industry coordinate to ensure that cybersecurity is prioritized within the development of 5G technology. The White House developed the National Strategy to Secure 5G and outlined how the Nation will safeguard 5G infrastructure domestically as well as abroad.
Regardless, the kind of improvements made to encryption and authentication of data in the recent versions of the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), many of the cybersecurity threats from the 4G era will persist. A good initiative could occur only when institutions and individuals join hands and work as a collaboration to prevent and mitigate these risks.
With faster connectivity, ultra-low intensity, 5G will redefine the operations of critical infrastructure activities from the plant floor to the cloud. It will enable large-scale connections and services that can pave the way for smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and other emergent technologies. But these capabilities also make 5G networks an easy target for criminals and foreign diplomats to exploit for valuable information and intelligence and even global disruption and can even raise cold war between the nations. 5G technology is a great achievement to feel grateful until risks associated with it are mitigated and people and organisations feel secure and satisfied. In the end, social benefit matters and not technological advancement.
References
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx%3Fg%3Dbc361bbb-1573-4577-9930-786f625e85eb&ved=2ahUKEwicjY24tPfxAhVeILcAHeYBBfUQFjAKegQIDRAC&usg=AOvVaw1t-f9paNxCxQGUpXxX_PsC
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.howtogeek.com/423720/how-worried-should-you-be-about-the-health-risks-of-5g/amp/&ved=2ahUKEwis3fbTtPfxAhWND94KHfHECbs4ChAWMAZ6BAgREAI&usg=AOvVaw2AI46pklGw0TrB9W34ZBUV
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-48616174.amp&ved=2ahUKEwicjY24tPfxAhVeILcAHeYBBfUQFjADegQIDxAC&usg=AOvVaw3rPQvFqFg7CUEO4W4nbuYw&cf=1
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7405337/&ved=2ahUKEwicjY24tPfxAhVeILcAHeYBBfUQFjAFegQIHRAC&usg=AOvVaw3Oe4wGWk48NCkYSq0Nnw85
Blog Posted By: Vaibhav Aggarwal, Student Risk Committee Member