One of the potential economic indicators in any region is transportation, logistics infrastructure, and its interconnectivity in that region. Most of the domestic goods and general public transportation takes place through road networks. Considering these factors, constructing safe and economical roads is quite challenging and risky within the expected time and allotted resources. The Cost of road construction per km is very high, approximately estimated to be around 5 – 15 crore rupees per kilometer depending upon the number of lanes, type of road, and road components (for example: “A Two– way Two-lane road with a median, footpath and appropriate road markings”). Therefore the entire phase in road construction risk assessment starting from Planning, Construction, to Operation and Maintenance takes a lot of Time and Resources. They are susceptible to risks due to large construction activities, complicated processes, seasonal changes, financial investments, demolition of existing structures, procurement of utilities, land acquisition, etc. Identifying potential risk parameters and their influence can optimize the risk in project constructions like-
- Reduced vehicle operating cost per kilometer length of the road.
- Optimized average travel time.
- Design safer roads to reduce accidents.
- The service life of roads can be improved.
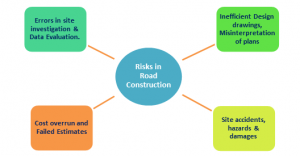
A risk is an uncertain or unforeseen circumstance that makes the project vulnerable to loss of capital, resources, and sometimes leads to hazardous unsafe situations for the working people. Delay in the planning and construction of infrastructure is also considered to be a risk factor in the economy and vision of the country[1].
Road Infrastructure: Risks and Management
Risk Classification & phases in project development:
Risks can be classified in many ways pertaining to the resources and objectives of the project, but the categorization of risks in a phased manner helps us in identifying its impact and finding solutions to reduce the risk. The risk management in road construction projects are broadly shown as;
Planning is the most important phase because and it defines the strategic development of any region in many ways like-
- Connectivity: Industries, Agriculture markets, Warehouses, Towns and Villages connected for transport goods as well as accessing the urban areas.
- Economic Importance: Decreasing the travel cost per kilometer, and also completing the project within the budget. It also creates economic zones and corridors.
- Prosperity and wellness of the country: Creating facilities for tourism, cultural and heritage spots
- Risks in Planning: Planning is done according to the objectives of the projects. There may be risks encountered during the planning and also while construction, due to the errors in the planning process. Planning related mistakes can lead to a huge loss if it is not rectified before construction. These risks may be due to human error or environmental constraints like- Topographical data, Site investigation, Poor design proposals, etc.
Risk Management in Planning: Most of the risks can be minimized by proper planning. It can be achieved by-
- Collecting accurate and reliable data from the previous projects and interpreting it to the existing project features.
- Minimizing the errors in the collection and creation of data sets (Ground Survey data, Socio-Economic Data, Existing features, and present road users data)
- Accuracy in detailed design drawings and specifications
- Experienced and Qualified professional acceptance in proposed plans.
Execution means the construction of the project after planning. It is a very intense and direct execution of every detailed proposal of the project. This phase entirely depends on the combination of – Construction Site conditions & Resources (Construction Materials, Machinery, Tools, Financial investments, and Workforce).
Some of the risks involved in construction are categorized below –
| Risks while Constructing Roads | Social Environment | -Delay in land acquisition, environmental clearances
-Political intervention, Local citizen interests |
| Stakeholders interest
& Contractor’s Organisation |
-Poorly defined and Sudden changes in project
-Poor communication and coordination between the parties |
|
| Financial Risks | -Loss-making bids in tenders
-Failed cost estimates due to service at remote locations -Delay in disbursement of bills and payment towards loans. |
|
| Inadequate site Conditions
& Failed Machinery |
-Hilly terrains, large water catchment areas, Congested and Traffic prone areas |
Risk Management while Construction: The above-mentioned risks occur due to various internal and external factors influencing the completion of the project and can consume months to years of duration according to the length of the road. The accidents or hazards can be managed and sometimes after the occurrence of the hazard or loss, it can be minimized by proper action of risk mitigation plans. Therefore a team of professionals who have experience in similar projects collectively create a plan for risk and coordinate with the contractors like-
- Clear and well-defined contractual agreements between the parties.
- Arbitrators to settle the disputes and communication gaps between the parties.
- Revision and approval of plans by independent engineers.
- Revising the cost estimates, compensations, traffic, taxes and also the cost of transport due to the project at remote locations.
- Allocation and arrangement of expenses at the right time can handle the risks and meet the project timeline.
- Safety protocols and standard operating procedures to minimize accidents to workers and protecting the equipment.
- Professionals teams to Assess. Review the plans, drawings and manage the construction activities.
- Efficiently managing the working conditions like in night time, traffic-congested areas, etc.
- Calling for the tenders for construction material suppliers to cut the expenses by monopolistic markets.
Phase 3: Operation & Maintenance
After construction, the projects are either handed over to the stakeholders to operate and maintain on their own or given on a contractual basis. Without the proper maintenance, the service life of the roads reduces and the roads are prone to deterioration and damages leading to inconvenience to the users and also create accidents. Such inabilities and failed operating procedures can be noted as risks and require proper road infrastructure management. Road operations include-Vehicular Traffic control, Maintaining the signboards and clear sight distances, Periodic check-ups and repairing if any damages, Keeping eye on the road inventories or establishments.
Operation and Maintenance risks:
- Sometimes operating costs and maintenance costs may increase resulting in low traffic revenue than expected. Regulating laws may be altered due to inefficient operating infrastructure.
- Air & Noise pollution levels also increase due to the poor operating standards
- Increased accident rates due to the non-maintenance of damaged parts of the road.
Risk Management in Operation & Maintenance:
- Feasibility studies to identify the risk-prone areas.
- Implementing the professional workflow in leading and controlling the operations.
- Effective budget prioritizing in operations and maintenance to check the financial risks.
- Consulting the professionals to set up safe and qualitative operating standards.
- Handling the workforce effectively.
Risk management has been classified into a hierarchy of stages where one can plan to avoid or minimize the effects of risks in road construction. These stages are organized based on the risk factors defined by organizations, experience, and expertise of workmanship, latest tools, and technology. The risk factors along with their duration and occurrences are studied and executed within the projected timelines by allocating resources (technical as well financial).
Huge losses can be seen when damages occur for which compensation may be relatively high.
Therefore some classical stages are followed while planning for risk management. They are,
- Defining constraints and delays as risks.
- Identify and assess the risks involved in the project by a survey on similar projects and other methods sophisticated to analyze the risks in previously collected data.
- Monitoring the risks to prepare Risk response plans and executing if risks are expected. It includes,
- Reviewing risks from the results of the analysis, the most critical risks are identified as planned.
- Elimination by modifying the existing plan and activities.
- Consultation & Mitigation by Inviting professionals to handle the risks that occurred to reduce its impact. Risks can also be shared with other parties to get the potential benefits within the timeline.
- Controlling the whole project by strategies or warning systems to identify and respond to the known risks.
- Accepting some unavoidable risks and planning for positive benefits from them.
Industrially accepted strategies are–
– Contractual Agreement defines all the obligations and requirements in the project and works as a tool to manage the risks.
– Feasibility studies by independent Engineers.
– Risks solutions from consultants.
– Brainstorming, Risk Matrix, SWOT analysis, etc., are some methods for risk assessments[2].
References:
- Chaitali S. Pawar, Suman S. Jain and Jalinder R. Patil (2015), “Risk Management in Infrastructure Projects in India”, International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced Engineering, Vol. 2, pp.172-176.
- P Szymański, Risk management in construction projects, Procedia Engineering -2017, vol. 208, pp.174-182
Blog published by: Sai Teja, Student Risk Committee Member












