“Cybersecurity is never just a technology problem, it’s people, processes and knowledge problems.” -NIST.
While most businesses today believe in cybersecurity, they might consider securing their networks, software, and assets against cyber-attacks and any data breaches. Often, they forget that the supply chain – either a typical manufacturer or service provider’s supply chain, is also vulnerable to security risks.
The Supply chain is extremely dependent upon geo-political factors, climatic factors, environmental issues, natural disasters and industry-wide shortages. During this era, supply chain risks are increasingly becoming diverse and therefore the disruptions can come from a good variety of sources, including physical damage at production facilities, natural disasters, strikes and labour disputes, capacity issues, delays, inventory stock problems and incorrect forecasts. Supply chain risk managementis becoming a top priority in procurement because losses from supply chain disruptions are extremely costly. Most of those factors are external which the business might not be ready to control. But cybersecurity riskscan often be treated and mitigated by the business.
The Covid-19 pandemic has caused immense changes and has affected the worldwide economy in a lot of ways. These rapid changes have led to disruption to business around the world. Now, companies are struggling to take care of security and business continuity programmes. The crisis has bought tons of changes within the way these companies and businesses operate. Businesses have accelerated the digitalization of their customers and supply chain interactions.
With this increasing dependence on IT within the businesses, cyber-crime cases are also expected to increase by 600% post Covid-19. These cyber risks also are increasing within the supply chain management. Interconnected supply chains can add to these risks. Within the year 2020, reports indicated that 40% of cyber-attacks originated from the extended supply chain.
An Efficient supply chain depends on fast, accurate and effective tracking of raw materials, productsand shipments wherever they’re within the world, this can be called Real – Time Tracking. Here a GPS tracking sends its location to the user and offers a real-time location that is updated every few seconds. Is it possible that this Real-time tracking can be hacked? If yes, how?
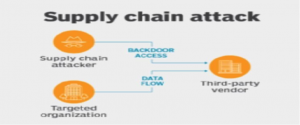
Well, it is possible that there may be a network or hardware that is delivered with malware installed or there may be any vulnerabilities in software easily discovered by malicious vectors. Also, smaller companies are often targeted by these malicious vectors as they’re more vulnerable to limitationsof resources and skills around cybersecurity. There may additionally be a case where your own software might not have a problem but the matter may lie with the solutions providers. Almost in every recent cyber-attack case, the root cause is identified as a cyber risk from the third-party supplier. The cyber risk can not only affect companies like FedEx, Gati, Amazon or Blue dart who majorly deal in supply chain management but also every other small or large businesses which have a weak IT infrastructure.
There are several ways and examples in which the supply chains are often hacked. One of the biggest cyber data breach examples is the Target breach. Target was the victim of the supply chain attack in the year of2013. The security was breached by one of the third parties. These credentials basically involved login details, passwords, addressesand all the other details of the network access to Target’s network system. The third party’s lack of maintaining security practices resulted in the theft of 70 million customers’ personal information. The after effect of this breach led tothe resignation of the CEO and a penalty of $200 million.
International cybersecurity risks also are increasing day by day. While China is the world’s production house there are a lot of dependent risks for all the countries and businesses depending on China. China is a communist country and has a lot of IT restrictions /transparency. So, in the same way,different countries may have different laws and regulations for their IT systems. If the IT regulations are not stringent enough, they will bea prey to the cyber risks in the supply chain.
Once the supply chain is breached and broken, there is often an incredible loss for the corporation which may lead to denial of services, data leakage, customer data theft, reputational risk and even an entire shut down of the business. These can be under control by undertaking various supply chain risk assessmentsby the organization.
So, the important question is-
What is the way to reduce the danger of loss? Let us look at the best practices in cyber supply chain risk management.
-GPS based location tracking must enhance security for transporting goods. This will help to reduce the danger of theft or other related losses.
-The company should start with basic cyber security education and a training program for both itsemployees and its suppliers.
-Bring your own device facilities within the supply chain causes tons of cybercrime issues especially with mobile devices because its tracking is often very difficult and therefore the level of malware protection on this device is insufficient.
-Limit access to data-Need to know basis. Employees should be able to access only those systems and data that they absolutely need to perform their jobs. All the activities can often be traced to a user, each employee should have a unique access ID that must be authenticated employing a robust password or passphrase, biometrics, or a token device or open-end credit.
-Physical access to systems and consumer data should be restricted to prevent employees and visitors from accessing or removing devices, customer data, systems, or hard copies.
-The company must have an adequate risk management system to reveal the problems by conducting a vendor risk assessment. To mitigate the vendor-related risks organizations should conduct a radical, annual vendor risk assessment and perform the specified due diligence with third-party relationships. Due diligence can assist you to identify what the vendor might require in terms of controls and monitoring.
-Defining data ownership requirements. Who maintains ownership of information being shared and what’s anacceptable use of that data? These questions can help the corporate to spot the most root explanation for their problems.
-Defining regulatory compliance requirements. Here the question would be, are their regulatory requirements that need to be met and maintained by both parties?
-Maintaining various sorts of incident response plans. Both parties ought to have a plan to notify each other if their network, systems or data are compromised or a compromise is suspected.
-Appropriate monitoring and internal control as well as external control plans.
To conclude, the third-party cyber security risk is indeed getting the recognition that it deserves however the efficient control implementation and ignorance towards it is not allowing the cyber risk to completely be addressed. In fact, these cases may likely add to affect supply chain management tremendously.
To safeguard this, every company should have a cyber crisis team thatcan rearrange resources and develop contingency plans with their supply chain risk management skills. Businesses should have a policy for their new suppliers and third parties. They need to also assess cyber risks to upgrade their internal technology before making any contracts.
Submitted By: Kajal Jani, Member of Student Risk Club (SRC)